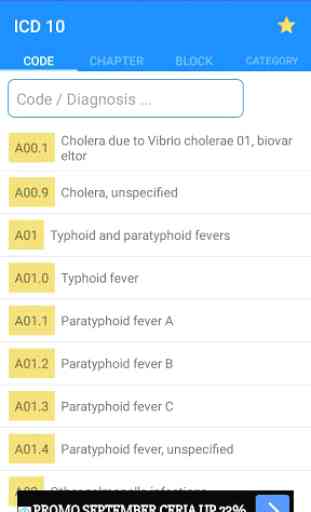
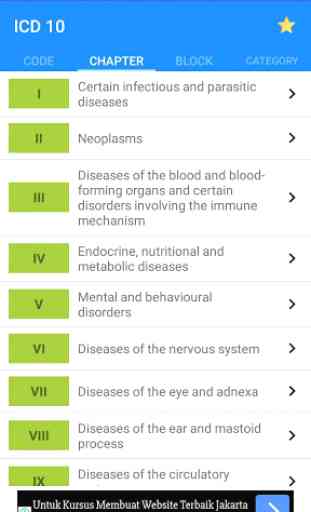
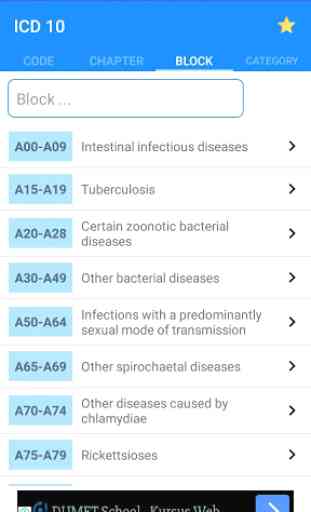
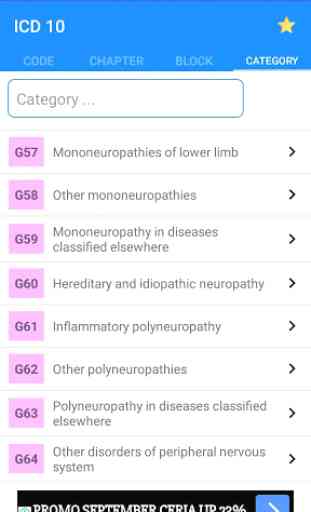
ICD 10 Code of Disease
A classification of diseases can be defined as a system of categories to which
morbid entities are assigned accordin
g to established criteria. The purpose
of the ICD is to permit systematic recording, analysis, interpretation and
comparison of mortality and morbidity data collected in different countries or
areas and at different times. The ICD is used to translate diagnoses of diseases
and other health problems from words into an alphanumeric code, which
permits easy storage, retrieval and analysis of the data.
In practice, the ICD has become the
international standard diagnostic
classification for all general epidemiological and many health-management
purposes. These include analysis of the general health situation of population
groups and monitoring of the incidence and prevalence of diseases and other
health problems in relation to other variables, such as the characteristics
and circumstances of the individuals affected. The ICD is neither intended
nor suitable for indexing of distinct clinical entities. There are also some
constraints on the use of the ICD for studies of financial aspects, such as
billing or resource allocation.
The ICD can be used to classify diseases and other health problems recorded
on many types of health and vital records. Its original use was to classify
causes of mortality as recorded at the registration of death. Later, its scope
was extended to include diagnoses in morbidity. It is important to note that,
although the ICD is primarily designed for the classification of diseases and
injuries with a formal diagnosis, not every problem or reason for coming into
contact with health services can be categorized in this way. Consequently,
the ICD provides for a wide variety of signs, symptoms, abnormal findings,
complaints and social circumstances that may stand in place of a diagnosis
on health-related records (see Volume 1, Chapters XVIII and XXI). It can
therefore be used to classify data recorded under headings such as ‘diagnosis’,
‘reason for admission’, ‘conditions treated’ and ‘reason for consultation’, which
appear on a wide variety of health records from which statistics and other
health-situation information are derived.
Source: www.who.int
Attribution: Icon made by Freepik from www.flaticon.com
morbid entities are assigned accordin
g to established criteria. The purpose
of the ICD is to permit systematic recording, analysis, interpretation and
comparison of mortality and morbidity data collected in different countries or
areas and at different times. The ICD is used to translate diagnoses of diseases
and other health problems from words into an alphanumeric code, which
permits easy storage, retrieval and analysis of the data.
In practice, the ICD has become the
international standard diagnostic
classification for all general epidemiological and many health-management
purposes. These include analysis of the general health situation of population
groups and monitoring of the incidence and prevalence of diseases and other
health problems in relation to other variables, such as the characteristics
and circumstances of the individuals affected. The ICD is neither intended
nor suitable for indexing of distinct clinical entities. There are also some
constraints on the use of the ICD for studies of financial aspects, such as
billing or resource allocation.
The ICD can be used to classify diseases and other health problems recorded
on many types of health and vital records. Its original use was to classify
causes of mortality as recorded at the registration of death. Later, its scope
was extended to include diagnoses in morbidity. It is important to note that,
although the ICD is primarily designed for the classification of diseases and
injuries with a formal diagnosis, not every problem or reason for coming into
contact with health services can be categorized in this way. Consequently,
the ICD provides for a wide variety of signs, symptoms, abnormal findings,
complaints and social circumstances that may stand in place of a diagnosis
on health-related records (see Volume 1, Chapters XVIII and XXI). It can
therefore be used to classify data recorded under headings such as ‘diagnosis’,
‘reason for admission’, ‘conditions treated’ and ‘reason for consultation’, which
appear on a wide variety of health records from which statistics and other
health-situation information are derived.
Source: www.who.int
Attribution: Icon made by Freepik from www.flaticon.com
Category : Medical

Related searches